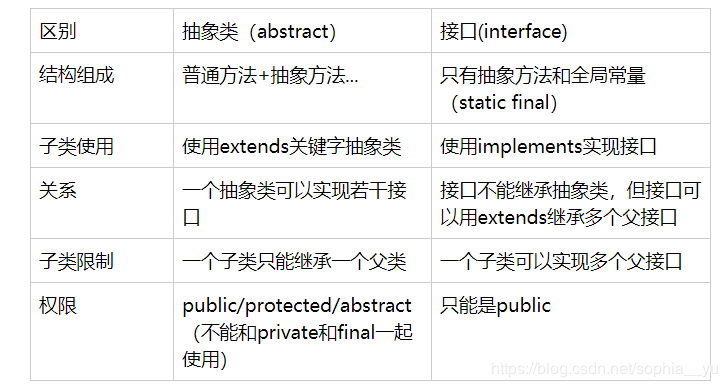
首先看一下异常的继承体系:
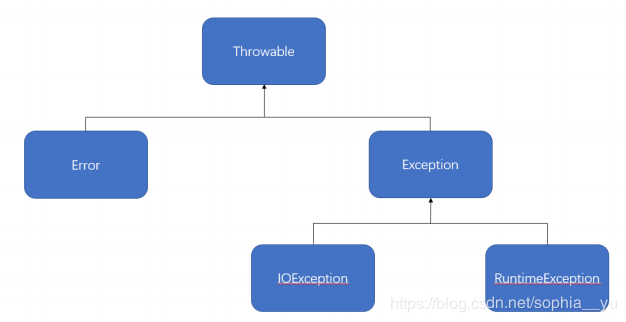
所有的异常都是由Throwable继承而来,我们来看他下面的两个子类Error和Exception.
Error (栈溢出异常):Error类描述Java运行时内部错误与资源耗尽错误。应用程序不抛出此类异常,这种内部错误(是JVM内部出现错误)一旦出现,除了告知用户并使程序安全终止之外,别无他法。
在Exception之下又分为两个分支,RuntimeException和IOException。
RuntimeException(运行时异常):由于程序出现错误导致的异常。
IOException :程序本身没有问题,但由于出现I/O问题导致的异常(比如:打开一个不存在的文件)
非受查异常:
继承于Error与RuntimeException类的所有异常子类称为非受查异常(不强制用户进行异常处理)
受查异常:
Exception以及IOException子类属于受查异常(强制用户进行异常处理,比如在写代码时代码那出现红线)。
如果一个程序出现异常:
package CODE;
public class Exception
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("1.计算前....");
System.out.println("2.计算式及结果:"+20/0);
System.out.println("3.计算完毕");
}
}

可以看到在出现异常后,异常语句产生之前的语句可以正常执行完毕,而异常产生之后程序直接进行了结束。
异常处理格式:为了保证程序出现异常后,也能正常执行下去,需要进行异常处理。
try{
有可能出现异常的语句 ;
}[catch (异常类 对象) {
//可以有多个catch
//出现异常后的解决方案
} ... ]
[finally {
//异常的出口,无论是否产生异常,均会执行finally 代码块
//即使try 或者catch存在return ,也会在try/catch return前执行finally代码块
}]
对于以上三个关键字,可以出现的组合:try…catch、try…finally、try…catch…finally
try…catch对异常进行处理:
package CODE;
public class Exception
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("1.计算前....");
try //try里放可能出现异常的语句
{
System.out.println("2.计算式及结果:"+20/0);
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) //异常类 异常对象
{
System.out.println("分母不能为0"); //出现异常解决方案,告诉用户分母不能为0
}
System.out.println("3.计算完毕");
}
}

以上代码虽然进行了异常处理,但是存在一个问题:你现在根本不知道程序产生了什么样的异常。所以为了明确的取得异常信息,可以直接输出异常类对象,或者调用所有异常类中提供的printStackTrace()方法进行完整异常信息的输出。
package CODE;
public class Exception
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("1.计算前....");
try //try里放可能出现异常的语句
{
System.out.println("2.计算式及结果:"+20/0);
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) //异常类 异常对象
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("3.计算完毕");
}
}
printStackTrace()会把异常完整信息输出,会把程序执行完毕,并且告诉用户出现什么异常,哪一行出现异常:

如果使用try…catch…finally进行处理:
public class Exception
{
public static int div(int a,int b)
{
System.out.println("1.计算前....");
try //try里放可能出现异常的语句
{
System.out.println("2.计算式及结果:"+20/0);
return 1;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) //异常类 异常对象
{
e.printStackTrace();
return 2;
}
finally
{
System.out.println("4.finally代码块");
return 3;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("返回值"+div(10,0)); //返回值是3,也就是说一定会走finally代码块
}
}
总结:
不管有没有异常,只有有finally,都会走finally代码块;
即使try 或者catch存在return ,也会在try/catch return前执行finally代码块;
如果finally中有return : 那么是finally 来return ;
如果finally中没有return : 如果有异常,则在catch中return ,如果没有异常,则在try中return (该谁return谁return )
如果通过命令行参数来给定操作数:
public class Exception
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("1.计算前....");
try //try里放可能出现异常的语句
{
int a=Integer.parseInt(args[0]); //将字符串转为整型
int b=Integer.parseInt(args[1]); //如果字符串中含有字母将会有异常
System.out.println("2.计算式及结果:" + a/b);
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) //异常类 异常对象
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("3.计算完毕");
}
}
注:在idea中输入命令行参数:[run]–>[Edit Configurations]—>[program arguments]。
对于上面代码,可能会出现下面异常:
用户没有输入初始化参数:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
用户输入的不是数字: NumberFormatException
被除数为0:ArithmeticExceptio
对于这些异常就需要一个一个catch:
public class Exception
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("1.计算前....");
try //try里放可能出现异常的语句
{
int a=Integer.parseInt(args[0]); //将字符串转为整型
int b=Integer.parseInt(args[1]); //如果字符串中含有字母将会有异常
System.out.println("2.计算式及结果:" + a/b);
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) //分母为0
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) // 输入不是数字
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) //没有命令行参数
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("3.计算完毕");
}
}
可是事实上并不知道有多少个异常或者catch 异常太繁琐,如果知道这些的异常的父类,可以直接用父类对象处理异常:
public class Exception1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("1.计算前....");
try //try里放可能出现异常的语句
{
int a=Integer.parseInt(args[0]); //将字符串转为整型
int b=Integer.parseInt(args[1]); //如果字符串中含有字母将会有异常
System.out.println("2.计算式及结果:" + a/b);
}
catch(Exception e) //分母为0
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("3.计算完毕");
}
}
Exception和RuntimeException区别
使用Exception是RuntimeException的父类,使用Exception定义的异常都要求必须使用异常处理,即Exception是受查异常;
而使用RuntimeException定义的异常可以由用户选择性的来进行异常处理,即非受查异常。
常见的RuntimeException:
ClassCastException(类转换异常)
IndexOutOfBoundsException(数组越界)
NullPointerException(空指针)
ArrayStoreException(数据存储异常,操作数组时类型不一致)
NumberFormatException(数值转化异常)